Exosomes
Autologous Exosomes for Hair Loss: An Innovative Solution
Understanding Autologous Exosomes
Exosomes are tiny extracellular vesicles released by cells that play a critical role in cell communication and tissue regeneration. Autologous exosomes refer to exosomes derived from the patient’s own cells, ensuring compatibility and minimizing the risk of rejection.

How Autologous Exosomes Work for Hair Loss
- Cell Communication: Exosomes contain proteins, lipids, and genetic material that facilitate communication between cells. They can enhance the activity of hair follicle stem cells, promoting hair growth.
- Regenerative Properties: Exosomes possess growth factors, cytokines, and microRNAs that can stimulate cellular repair and regeneration. This is particularly beneficial in addressing hair thinning and loss.
- Mechanism of Action:
- Enhancing Blood Circulation: Exosomes improve local blood circulation, ensuring follicles receive essential nutrients and oxygen.
- Reducing Inflammation: They can modulate inflammatory pathways, which are often involved in hair loss conditions like alopecia.
- Supporting Follicle Survival: By promoting survival and proliferation of hair follicle cells, exosomes can potentially reverse the hair loss process.
Comparing Autologous Exosomes to PRP Therapy
What is PRP Therapy?
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy is a rejuvenating treatment that utilizes a patient’s own blood components to stimulate hair growth. The process involves drawing blood, processing it to isolate growth factors within the plasma, and injecting it into the scalp.
Key Differences Between Autologous Exosomes and PRP
- Composition:
- Autologous Exosomes: Rich in bioactive molecules, they provide advanced cellular communication tools and regenerative capabilities.
- PRP: Concentrated platelets contain growth factors but lack the extensive molecular components found in exosomes.
- Mechanism of Action:
- Exosomes: Work primarily through cellular signaling, enhancing the natural reparative processes of hair follicles.
- PRP: Focus on delivering growth factors directly, which may not effectively address the deeper cellular mechanisms involved in hair loss.
- Treatment Process:
- Exosome Therapy: Involves collecting cells (typically from adipose tissue), isolating exosomes, and then injecting them into the scalp.
- PRP Therapy: Involves blood draw, centrifugation, and injection of PRP into the scalp.
- Treatment Efficiency:
- Exosomes: Studies suggest that exosome therapy may yield quicker and more effective results, thanks to their multifaceted molecular action.
- PRP: While effective for many, some patients may experience slower results or limited improvement.
Conclusion: Is Autologous Exosomes the Right Choice for You?
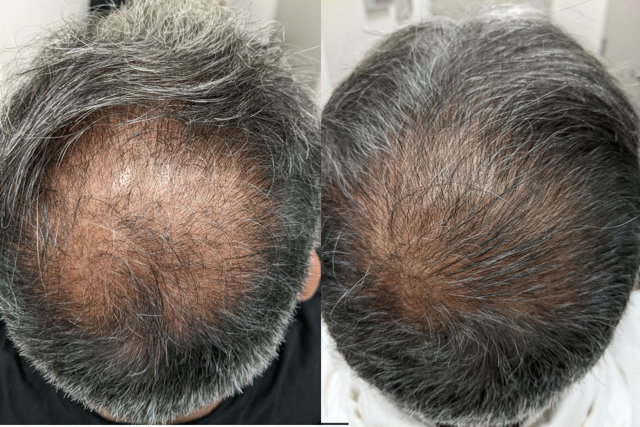
As hair loss becomes a growing concern for many individuals, advanced treatments like autologous exosomes are paving the way for innovative solutions. By harnessing the power of cellular communication, they offer a potentially more effective approach compared to traditional PRP therapies.
Why Choose Autologous Exosomes?
- Minimally Invasive: As a non-surgical treatment, exosome therapy is less invasive and can be performed in-office.
- Personalized Treatment: Derived from your own cells, the risk of side effects is significantly reduced.
- Holistic Approach: With their diverse role in cellular signaling, exosomes may promote overall hair health and rejuvenation.
If you’re considering options for hair restoration, consult with our Trichologist to discuss the benefits of autologous exosomes and determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
